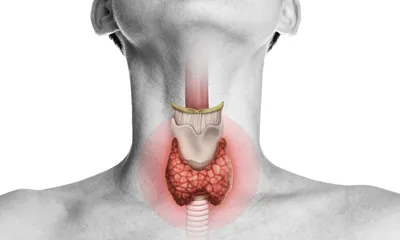
Hypothyroidism
-
Description
-
Signs & Symptoms
-
Anatomy
-
Cause
-
Diagnosis
What is Hypothyroidism?
When a person has an underactive thyroid gland that is not producing enough thyroid hormone they are said to have hypothyroidism. Thyroid hormone is essential for energy regulation in cells, and so a healthy functioning thyroid gland is very important for overall health. Without one a person’s metabolism will slow down when they have hypothyroidism. Myxedema is when thyroid hormone levels in the body get extremely low and result in a potentially life-threatening condition with the possibility of heart failure or coma.
Hypothyroidism is more common for older adults, and most notably with post-menopausal women compared to men of the same age range. Hypothyroidism left untreated over many years may have very pronounced health effects for people, but signs of the condition will usually prompt the sufferer to get a doctor’s opinion early on in their development of it and in these instances hypothyroidism is a very manageable condition.
What Causes Hypothyroidism?
This condition is going to have primary or secondary causes, and primary causes for hypothyroidism are much more common. The most prevalent of them is Hashimoto’s disease where the body’s immune system starts to attack and damage the thyroid. It can also be hereditary as a medical condition where it is passed down through your family. Secondary causes like severe iodine deficiencies can also be behind what causes hypothyroidism. In these instances, high-dose dietary supplementation can usually alleviate symptoms.
Women who are pregnant become more prone to developing Hashimoto’s disease, and this is why hypothyroidism can start during pregnancy. Thyroid hormone is a key part of brain and nervous system development in fetuses and if a woman has hypothyroidism while pregnant she will need to be on a medication for an underactive thyroid. Birth control pills can alter thyroid hormone production too but will increase hormone levels rather than lower them. This is something women will need to discuss with their doctor if they’re using an oral contraceptive.
Hypothyroidism Symptoms
There are definitive signs when someone has an underactive thyroid gland. Unexplained weight gain, depression, and body soreness are three of the common early low thyroid indicators that people start to experience. Other hypothyroidism symptoms include:
- Chronic fatigue
- Elevated cholesterol
- Constipation
- Cold intolerance
- Dry and / or coarse skin and hair
- Heavy menstrual periods for women
- Brain fog
- Decrease in sex drive (libido)
- Voice hoarseness
- Facial puffiness
Untreated hypothyroidism may result in cardiac health problems or developing a goiter, which is when the thyroid gland becomes grossly enlarged in size. Untreated hypothyroidism can also cause poor mental health.
Hypothyroidism Treatment
The most conventional approach to hypothyroidism treatment is to have the patient on a medication like Synthroid or Cytomel that will promote increased hormone production from the thyroid gland. A doctor will often recommend a hypothyroidism diet as part of treatment too, and this is often if they suspect iodine deficiency is worsening thyroid disease symptoms. Foods that are high in iodine are meat, poultry, and seafood, eggs, dairy products, and laver (edible seaweed).
Signs & Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin
- Constipation
- Hoarseness
- Muscle weakness
- Elevated blood cholesterol level
- Puffy face
- Thinning hair
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Depression
- Impaired memory
Anatomy
- Thyroid gland
- Pituitary gland
- Hypothalamus
- Metabolic system
- Heart
- Liver
- Muscles
- Skin
- Hair
Cause
- Autoimmune disease (Hashimoto's thyroiditis)
- Thyroid surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Certain medications
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Pituitary disorder
- Iodine deficiency
- Pregnancy
- Infiltrative diseases (e.g., amyloidosis, sarcoidosis)
Diagnosis
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test
- Free thyroxine (T4) test
- Anti-thyroid antibodies test
- Thyroid ultrasound
- Radioactive iodine uptake test
- Cholesterol test
- Complete blood count (CBC)