Can the Thyroid Affect Mental Health
Mental health conditions have been highly stigmatized in many cultures and societies for centuries. Although they are still often misunderstood, they are now discussed more openly than in the past, which helps affected people access treatment and feel less isolated. Just like physical conditions, mental health issues can have various causes, including unresolved trauma, stressful life experiences, social isolation, genetics and chemical imbalances in the brain. Additionally, certain chronic illnesses like diabetes, vitamin B12 and D deficiencies, infections, sleep disorders, and hormonal imbalances can also cause mental health issues. This may lead you to wonder: Can the thyroid affect mental health as well?
By reading this article, you will learn about the thyroid’s role in the human body. With this, you will also find out whether the thyroid can cause mental health issues, and how to treat mental health problems caused by thyroid imbalances.
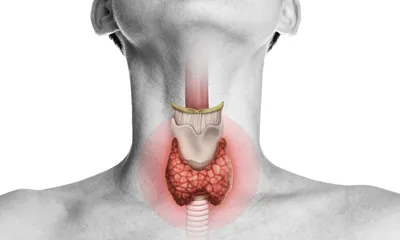
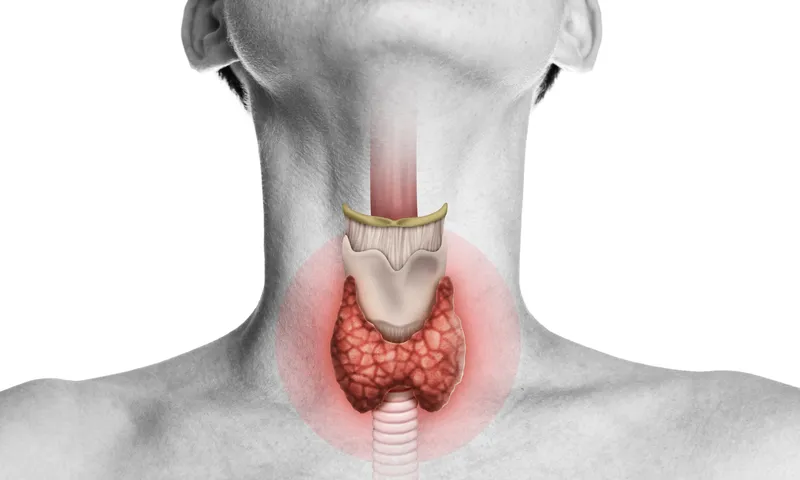
The Thyroid’s Role in the Body
Given that the thyroid isn’t as well-known as other similarly vital organs such as the pancreas, kidneys or liver, its high level of involvement in many essential body functions may be surprising to some. The thyroid gland significantly influences many processes by producing two main hormones: thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Doing so, it not only plays an important role in regulating metabolism and body temperature, but it’s also vital for reproductive health and digestive function, as well as heart rate and blood pressure regulation. Finally, it affects normal growth and development in children, brain function, and mood.
Can the Thyroid Affect Mental Health?
Because of its essential role, impaired thyroid function can cause significant disruption in the body. The two most common thyroid conditions are hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), which happens when the thyroid produces too few of its main hormones, and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), which occurs when the thyroid makes excess hormones. The former is the most common thyroid disorder globally and is often associated with symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, and hair loss. In contrast, hyperthyroidism is characterized by a rapid heartbeat, excessive sweating, tremors, and frequent bowel movements. If these and other thyroid disorders remain untreated long-term, more serious health issues like heart problems, fertility issues, and bone loss can follow.
However, besides these physical symptoms, the thyroid can also affect mental health. An underactive thyroid is known for causing depression, low levels of energy, memory problems, and slowed thinking. In contrast, an overactive thyroid often comes with anxiety, irritability, restlessness, insomnia, and mood swings. Mental symptoms occur since thyroid hormones influence brain chemistry and neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
How to Address Mental Health Issues Caused by Thyroid Imbalances
When addressing mental health issues caused by thyroid disorders, the appropriate treatment method depends on the nature of the thyroid condition. Therefore, a proper diagnosis by determining TSH, T3, and T4 levels through blood tests is crucial. When hypothyroidism is the cause of your symptoms, your doctor will likely prescribe you thyroid hormone replacement such as Synthroid and Cytomel. In contrast, hyperthyroidism is often treated with antithyroid medications like Tapazole, radioactive iodine, or surgery.
If your thyroid disorder affects your mental health, psychiatric medications may be beneficial in some cases, but only alongside thyroid treatment. This also applies to other supportive, mood-stabilizing measures that can aid your recovery, including restful sleep, proper stress management, physical exercise, and a balanced diet. Working closely with your endocrinologist and mental health professional and regularly following up with them can help keep your thyroid hormone levels in check and prevent mental health symptoms from returning.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The above information is intended to increase awareness of health information and does not suggest treatment or diagnosis. This information is not a substitute for individual medical attention and should not be construed to indicate that use of the drug is safe, appropriate, or effective for you. See your health care professional for medical advice and treatment.