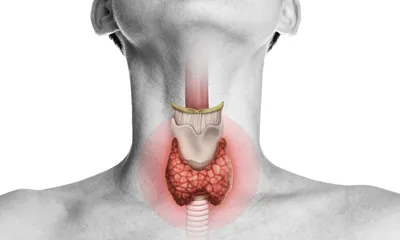
Thyroid Health
-
Description
-
Signs & Symptoms
-
Anatomy
-
Cause
-
Diagnosis
How to Improve Thyroid Health
Your thyroid gland is located in your neck and serves as part the endocrine system in the body. Its job is to regulate energy metabolism so that cells get the energy they need to work properly, and this makes the thyroid integral to overall health and the body’s continued ability to function properly. It is controlled by the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland in the brain, but an underactive (hypothyroidism) or overactive (hyperthyroidism) thyroid can cause health problems because of too little or too much thyroid hormone.
Anyone asking how to improve thyroid health can first understand the need to eat more of certain foods, and less of others. This is because inflammation of the intestinal tract can be a contributor to thyroid problems. Avoiding environmental toxins may be a focus too if someone is concerned about their thyroid health.
What to Take for Thyroid Health
In addition to the mineral and vitamin supplementation indicated above, it may also be helpful to take Rx medications for thyroid health. Ones like Cytomel and Thyroid Armor are often prescribed for hypothyroidism and treating an underactive thyroid. For hyperthyroidism a doctor may be prescribing Tapazole or something similar.
Thyroid Health Supplements
Iodine deficiency is one of the primary reasons for an underactive thyroid, and if that’s the case then taking iodine supplements is going to be the approach for hypothyroidism treatment. The same goes for Vitamin D and Selenium supplementation, plus taking probiotics for better gut health. Natural cure approaches are also a possibility with thyroid health supplements too.
There are some who have experienced a better functioning thyroid after taking ashwagandha root, aloe barbadensis Miller juice, royal jelly, green barley grass, or taraxaf (a combination of olive and nettle leaves, curcumin, and dandelion). Acupuncture for thyroid health may also be a beneficial treatment for people with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Foods for Thyroid Health
Eating more fruits, vegetables, beans, whole grains, fish and seafood, nuts and seeds, and healthy oils may be recommended for people with poor thyroid health. Good examples of these foods are:
- Chicken
- Tuna
- Turkey
- Shrimp
- Hard-boiled eggs
- Cottage Cheese
- Brazil nuts
Adhering to the Mediterranean Diet is also known to be in line with a better functioning thyroid. There will be foods to avoid if you have an underactive or overactive thyroid, and especially processed foods and ones with lots of sugar or preservatives that will make the gut lining inflamed and contribute to a poor-functioning thyroid gland. Excess consumption of cruciferous vegetables may also be harmful if you have either condition, and you may want to consider not eating Cassava root if you are experiencing thyroid dysfunction.
Signs & Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin
- Constipation
- Hoarseness
- Muscle weakness
- Elevated blood cholesterol level
- Puffy face
- Thinning hair
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Depression
- Impaired memory
Anatomy
- Thyroid gland
- Pituitary gland
- Hypothalamus
- Metabolic system
- Heart
- Liver
- Muscles
- Skin
- Hair
Cause
- Autoimmune disease (Hashimoto's thyroiditis)
- Thyroid surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Certain medications
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Pituitary disorder
- Iodine deficiency
- Pregnancy
- Infiltrative diseases (e.g., amyloidosis, sarcoidosis)
Diagnosis
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test
- Free thyroxine (T4) test
- Anti-thyroid antibodies test
- Thyroid ultrasound
- Radioactive iodine uptake test
- Cholesterol test
- Complete blood count (CBC)